How Secure Mobile File Storage & Sharing Refines Your BYOD Strategy
Includes best practices and legal issues in relation to mobile file transfers, storage, and sharing in a BYOD setting.

Overview
Pretty soon, your business will have to adopt some form of BYOD policy. That policy is bound to include several provisions for securing company-owned data that may have found their way into your employees' personal mobile devices. Among many others, you'll also need to establish guidelines for secure file transfers, storage, and sharing in order to protect that data.

Although protecting company data is something you've probably been doing for ages, BYOD is a whole new beast altogether. In BYOD, you'll have to secure that data while making sure you don't step on the rights of your workforce.
Inevitability of BYOD
We're at an age where people can easily and just simply love to share photos, videos, thoughts, and even mundane experiences with other people on the Web. Look around you. I bet many employees in your organization are on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+, YouTube, Vine, Instagram, and other social networking sites many times a day.

This is the age of the millenials, a generation born in the early 80's to late 90's. That means, in the workplace, they're the employees in their early 20's to early 30's. These are the people who, in a short span of time, are going to be taking over various positions in our companies. In fact, many of them are already influencers, if not decision makers, in their respective organizations.
Most millenials have this constant urge to "stay connected" and are difficult to separate from their mobile devices. While other people view this as a liability, many business leaders have actually seen an opportunity.
These executives believe that by allowing employees to bring the mobile devices they love - devices that are practically handheld computers - into the workplace and use them for work-related activities, they can significantly improve collaboration, agility, innovation, and productivity.
These compelling reasons, added to the continuing influx of millenials into key positions in the workplace, makes BYOD adoption simply inevitable.
Risks of bringing personal mobile devices into the workplace
While BYOD brings a bunch of benefits, it also bears with it a bundle of security issues that weren't there before.
Mixing company and personal data
For example, in the past, if you looked into a locked-down, company-issued BlackBerry, you would most likely find only work-related data. But today, if you look into a personally-owned Android or iOS device used in a BYOD environment, you'll also discover lots of personal files. Mixing enterprise data with personal data is already a security breach just waiting to happen. A company spreadsheet unintentionally attached to a personal email can lead to unauthorized disclosure of what may be confidential information.
Insecure networks
Today's mobile devices are typically packed with excellent wireless connectivity features (WiFi, LTE, HSDPA, EDGE, etc.) and backed by Internet-hungry data plans. So users can easily connect to the Web and stay connected for long periods of time from almost anywhere - in the office, in a restaurant, coffee shop, airport, train, terminal, subway station, or at home.
This always-on connectivity actually presents serious vulnerabilities because many of these connections are made over public networks; outside the protection of the company firewall. What makes things worse is that the same insecure networks are often used in sending work-related data to officemates, making the data vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks if no encryption is employed.
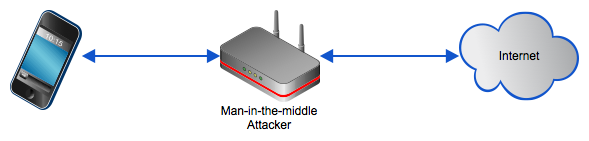
Susceptibility to loss or theft
Smartphones and tablets are designed to be ultra-portable. In the context of our discussion, that can be a bad thing. The small sizes of these devices make them susceptible to getting misplaced or stolen.
The presence of this risk can be confirmed by running a quick search at privacyrights.org which reveals that in the last 30 months (2011 to June 2013), the number of reported data breaches due to lost or stolen portable devices averaged at an alarming 9.1 incidents per month.
Because mobile devices can easily fall into the wrong hands and consequently put company data at risk, most companies who set out to implement a BYOD policy include "remote wipe" to their must-have capabilities.
Why remote wipe is crucial to any BYOD policy
A remote wipe is a security feature that allows you to delete practically everything in a mobile device even if that device is not with you. This can come in handy if an employee's device gets lost and you've concluded that there's no way it can be retrieved anymore. One example of a remote wipe solution is Apple's own Find My iPhone app.
Once you activate a remote wipe, all the emails, SMS messages, applications, and practically everything else stored in that device will be wiped out. That means, anyone who gets hold of the device will no longer be able to see whatever data was once stored there.
This capability is extremely important because you'll never know what company-owned data may be stored in your employees' mobile devices. A remote wipe will ensure that no confidential information falls into the wrong hands.
But there's a hitch.
The problem with a remote wipe is that it's a point of no return (although that's supposed to be the whole point, right?).
Chances are, any company data that's been stored in an employee's mobile device is just a copy of something that's already in your company's servers. But what about your employee's personal files? What about those pictures of his first-born's 1st birthday? Pictures of his wedding? Videos of his latest vacation?
This can actually be a point of contention and a potential magnet for lawsuits.
How does a secure mobile file storage help?
One way of avoiding those nasty lawsuits is by integrating a secure mobile file storage system into your BYOD policy. By providing an online server onto which your employees can upload and store files and making it part of an end user backup policy, you can avoid the dilemma of having to execute a remote wipe on a missing device that contains files with no backup copies.
Of course, the server has to be equipped with all the necessary features to ensure a secure file transfer. Otherwise, the files in that server can be sitting ducks to cyber crooks.
First, it has to support secure file transfer protocols like (https, ftps, or sftp), which encrypt files as they are sent over the network. You'll need a compatible secure file transfer client that supports the same protocols for this to work. The server also has to provide a mechanism for encrypting files as they are stored on the server itself.
For a list of essential attributes of a secure file transfer, click that link.
Once you have a server like this, your employees can also use it to perform secure mobile file sharing. You can grant a set of users access rights to a common folder so that any one of those users can upload files from his phone to the server and then another user can download the same files to her own device.
But you know what's an even better set up? If this server is the same server that already provides secure file transfer services to all "regular" endpoints, i.e., desktops and laptops. That way, you can have a highly collaborative and productive environment. An employee can upload a spreadsheet from his desktop to the server and his boss can securely download that same file to his smartphone while waiting for his flight at the airport.
So am I describing a cloud-based file sharing service like DropBox? No.
Mobile file storage is most secure when you're in full control
- When you subscribe to a cloud-based file sharing service, your files are going to be in the hands of a third party. There are many security issues here. Here are a few of them:
- That company will also be serving several other clients. You don't know what kind of segregation (if ever) is being implemented to ensure that your files are insulated from theirs.
- Some of these cloud companies store or backup their data at datacenters located overseas; some in countries that have very weak legislations on data privacy and protection (if any at all).
- You have no idea what level of security is being implemented on the physical servers themselves. Remember, the people who will be maintaining those physical servers don't belong to your organization.
- If you're operating in a regulated industry, you should know whether the cloud provider is also compliant. Some regulations, like the latest version of HIPAA for example, have security requirements that also apply to business associates.
- How reliable is their Business Continuity/Disaster Recovery plan? Their downtime can become your downtime too.
- There might be instances (e.g. a sophisticated data breach or fraudulent activity) when you might want to conduct your own investigations on their servers. Will they allow you to do that? Or do they have sufficient logs to assist you in your data forensics?
- You have no idea who else are being granted access to your data. I won't be mentioning anyone here but you should really be reading the news!
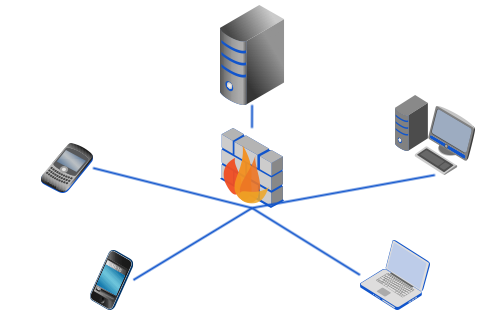
The most secure way to implement a mobile file storage system is by using a Managed File Transfer Server administered by your own server admins. For full control, you will want to deploy that MFT server on-premise, i.e., behind your corporate firewall.
Now, if you're not very paranoid, you can have a virtual instance of your MFT server hosted in the cloud by an IaaS provider. The key difference between this set up and the usual cloud-based (SaaS) file sharing service is that your admins will be totally in charge of configuring security settings like granular access control, encryption keys, IP-based access, authentication, password strengths, and many others.
Summary
An MFT Server administered by your own network engineers can provide the most secure environment for storing and transferring files and enable your employees to collaborate securely under a BYOD setting. It can also help you avoid legal complications by enabling users to upload both company-owned files and personal files for backup purposes.
JSCAPE MFT Server client for iOS
JSCAPE has recently made it's free iOS file transfer client available for download from the iTunes App Store. The newly released client allows users to connect to JSCAPE MFT Server from their iOS devices (iPhone/iPad/iPod Touch) for use in securely viewing, transferring, organizing and sharing files and is available to those running JSCAPE MFT Server Enterprise 8.7 or above.